Blockchain networks record a lot of valuable information, like every token transfer, smart contract interaction, NFT mint, and DAO governance vote. Even though the data is permanent, it’s often spread across different chains and stored in different formats. If you want to pull data from multiple networks, you might have to run your own nodes, write custom indexing code, or depend on external services that may not be reliable.
Chainbase is building a hyperdata network that pulls together data from different blockchains, organizes it, and makes it easy to work with. This lets developers create data-driven applications such as AI tools, DeFi analytics dashboards, and cross-chain wallets more efficiently and with fewer technical barriers.
What Is Chainbase (C)?
Chainbase is a decentralized data infrastructure network founded in 2021. Its main purpose is to collect, structure, and deliver blockchain data from hundreds of networks in a way that is easy to use for developers, projects, and businesses. The platform provides a unified solution for accessing both on-chain and off-chain data, making it possible to analyze, build, and innovate without the barriers of data fragmentation.
Think of Chainbase as a hub that connects to multiple blockchains and gathers their data into one place. Through its APIs and developer tools, users can access real-time information across different chains for things like DeFi analytics, NFT tracking, smart contract monitoring, and more. This approach is designed to support a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance, Web3 analytics, and AI-driven crypto tools.
Chainbase aims to solve the common problems of blockchain data—such as inconsistency, lack of structure, and limited accessibility—by standardizing how data is collected and shared. The platform also allows participants to contribute to the network and be rewarded for processing, validating, or improving data quality.
How Does Chainbase Work?
Chainbase is powered by a dual-chain architecture that combines Cosmos and EigenLayer. The platform operates through a four-layer system, with each layer handling a specific part of the data journey.
Data accessibility layer
Chainbase collects and organizes data from both on-chain and off-chain sources. On-chain data includes information like transaction histories and
smart contract interactions, while off-chain covers larger or more private information like AI models or app metadata that are stored in decentralized systems.
The data comes from a network of decentralized providers, so no single party has control. The platform is also able to verify the accuracy of data without revealing any sensitive information with zero-knowledge proofs (
ZKP).
Co-processor layer
This layer is powered by
manuscripts, which is a core concept of the Chainbase ecosystem. A
manuscript is a script that defines how blockchain data should be processed, like what to extract or how to clean and format it in a way that apps and AI tools can use.
For example, a developer might write a
manuscript that filters out the token transfers from a smart contract or tracks wallet behavior patterns for fraud detection.
Once the
manuscript is published to the network, anyone can use it and the original creator earns rewards each time it’s used. It’s a way for developers to turn their knowledge into something valuable and reusable. As more developers contribute, the platform evolves into a growing library of trusted, ready-made data tools that anyone can plug into.
Execution layer
The Chainbase Virtual Machine (CVM) is a custom-built environment designed for executing
manuscripts at scale. It uses data and task parallelization to handle multiple jobs at once and enable fast and efficient processing even at scale.
This layer is secured by EigenLayer, which lets Autonomous Verifiable Services (AVS) node operators restake ether or liquid staking tokens (LSTs) to provide the computing resources needed. They help keep the network decentralized and secure and are rewarded based on how much work they do.
Consensus layer
Chainbase uses CometBFT, a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (
BFT) consensus algorithm that offers fast and reliable finality. It also uses a Delegated Proof of Stake (
DPoS) system, where validators check data operations and ensure everything stays consistent, while delegators can support trusted validators by staking their tokens.
What Is Chainbase Token (C)?
C is the native utility and governance token of the Chainbase network. It is used as the primary means of payment, reward, and participation within the Chainbase ecosystem.
Holders of C tokens can use them for several purposes:
Accessing Data: Users pay C tokens to access and query datasets or to use APIs on the platform.
Incentives and Rewards: Operators, developers, and validators receive C tokens as rewards for their contributions to data processing, validation, and network maintenance.
Staking: Both Operators and Validators must stake C tokens to secure their roles in the network. Delegators can also stake C tokens with Operators or Validators, earning a share of network rewards.
Governance: C token holders have the right to vote on important decisions and proposals, including upgrades, changes to rewards, and other network policies.
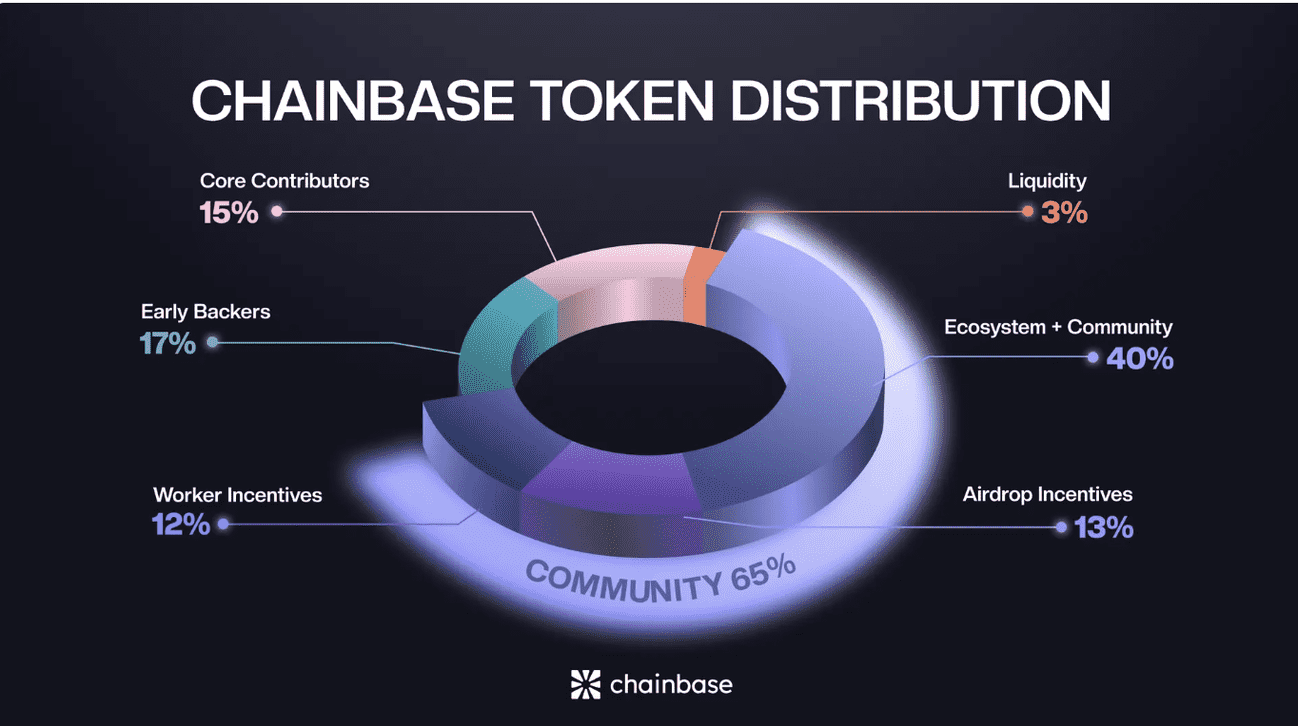
The total supply of C tokens is capped at 1 billion. Most of the tokens are distributed to the community, operators, developers, early investors, and for ecosystem incentives.
How to Get Free C Token Airdrop
Chainbase has launched airdrop campaigns as a way to reward early supporters and attract new users to its network. If you are interested in receiving free C tokens, there are a few main ways you can participate, depending on the latest community events and campaigns.
Official Airdrop Campaigns
Chainbase may organize airdrop events on its official website or airdrop portal. By registering, completing identity verification (KYC), and following specific instructions, such as making a deposit or using the platform, you could become eligible for C token rewards.
Trading and Activity Challenges
From time to time, Chainbase or its partners run events where users can earn C tokens by trading, completing certain tasks, or achieving volume milestones. Details and requirements vary by campaign, so checking the latest rules is important.
Referral Programs
You might also receive C tokens by inviting friends to join Chainbase and participate in airdrop activities. Both you and your referrals can be rewarded if the referral process is completed according to the campaign guidelines.
Community and Development Engagement
Early testers, active community members, or developers who contribute to the Chainbase ecosystem may be eligible for airdrop rewards. Activities could include testing features, providing feedback, or building with Chainbase tools.
Always check the official Chainbase website or community channels for the latest information about airdrop opportunities. Use caution and only trust official sources to protect yourself from potential scams.
Conclusion
Getting useful data from blockchains is difficult when you are dealing with multiple networks and different data formats. Chainbase is designed to make that process easier by turning scattered blockchain data into something clean, structured, and ready to use.
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.