DeFi can give users different ways to earn on their crypto holdings, but finding steady, reliable returns isn’t easy. Interest rates for lending the same asset (like ETH) differ between DeFi protocols, and there is no common benchmark to compare your options.
This lack of consistency makes it hard to manage risk or carry out long-term income strategies. Treehouse aims to address this by creating a fixed income layer for digital assets, starting with Ethereum, to help you earn more stable, predictable returns over time.
What is Treehouse (TREE)?
Treehouse is a decentralized finance protocol focused on building the fixed income layer for digital assets. The platform introduces two main innovations: Treehouse Assets (tAssets) and Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR), both designed to unify and standardize yields across DeFi and support the creation of robust on-chain fixed income products.
How Treehouse (TREE) Works
Treehouse operates through several breakthrough technologies that democratize fixed income access and standardize DeFi yields:
tAssets: Unified Yield-Bearing Tokens
When users deposit crypto assets like ETH or stablecoins, they receive special tokens called tAssets (such as tETH) that automatically earn unified yields from multiple DeFi protocols. These tokens handle yield optimization and arbitrage behind the scenes, removing the need for users to hunt for the best rates across different platforms.
DOR: Decentralized Offered Rates
Treehouse calculates and publishes benchmark interest rates through a consensus mechanism involving trusted panelists like RockX and other institutional staking providers. DOR acts as the "LIBOR for DeFi," enabling confident pricing and innovation for fixed income products like bonds and swaps.
Interest Rate Arbitrage Engine
The protocol actively monitors and exploits rate discrepancies between lending and staking opportunities across DeFi platforms. When different protocols offer different rates for the same asset, Treehouse automatically reallocates capital to maximize returns and bring efficiency to fragmented yield sources.
Advanced Analytics Dashboard
Users get comprehensive portfolio visualization, real-time earnings tracking, risk analytics, and performance breakdowns in plain language. The platform provides institutional-grade risk metrics and management tools previously unavailable in DeFi.
Cross-Platform Integration
Treehouse operates on Ethereum and BNB Smart Chain with analytics solutions deployed across multiple networks. The platform integrates with Web3 wallets and supports usage across other DeFi protocols like Aave and Silo V2.
What Are Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR)?
DOR (Decentralized Offered Rates) are on-chain benchmark interest rates for digital assets, much like how traditional finance relies on reference rates such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). In simple terms, DOR helps answer the question: “What’s a fair, reliable average lending rate for ETH?”.
Instead of guessing or relying on one source, DOR is built through a community-driven consensus process, where different participants come together to share rate data and keep things transparent. The stakeholders in the DOR ecosystem include:
-
Operators: These are the coordinators of the system. Treehouse, for example, acts as the first Operator, responsible for launching and maintaining the benchmark rate feeds.
-
Panelists: These are specialized entities, like market makers or staking platforms, that supply interest rate data or forecasts using Treehouse’s tools.
-
Delegators: Regular users who delegate their tAssets to Panelists. They maintain ownership of their assets while letting trusted participants submit rate data on their behalf, similar to staking delegation.
-
Referencers: These are platforms like DeFi protocols, exchanges, or lending apps that use DOR as a pricing reference for their products.
tETH
tETH is a token you receive when you deposit ether or liquid staking tokens like stETH into the Treehouse protocol. But it’s more than just a wrapper for your assets. tETH actively searches for the best yield opportunities across the Ethereum ecosystem and uses arbitrage to boost your returns.
For example, if ether staking rewards are higher than borrowing costs on a lending platform, the protocol takes advantage of that difference and passes the extra yield back to you. So rather than manually moving your ether between platforms to chase better returns, tETH does the work for you.
tETH holders also earn points through Treehouse’s rewards program, which gives additional incentives to early tETH holders and Treehouse users.
tETH Risks
Treehouse has pointed out a few important risks to keep in mind when using tETH since it interacts with both staking and lending platforms.
One major risk is the potential collapse of an underlying protocol, whether it’s a liquid staking service or a lending platform. There’s also the risk of a sudden drop in the value of staked assets, known as a depeg, which could trigger liquidations and lead to losses.
Other potential issues are bugs in the smart contracts, inaccurate data from blockchain oracles, and lending pools becoming overcrowded. When that happens, borrowing costs can increase and reduce the returns you earn from tETH.
How Treehouse Helps Protect Users
Treehouse has implemented multiple safeguards, including a contingency plan for significant depegs, a dedicated insurance fund to cover unexpected losses, and a Protocol-Owned Peg Protection (PPP) mechanism that buys up undervalued tETH during volatile markets. These measures work together to enhance user protection while supporting the long-term foundation for fixed income in DeFi.
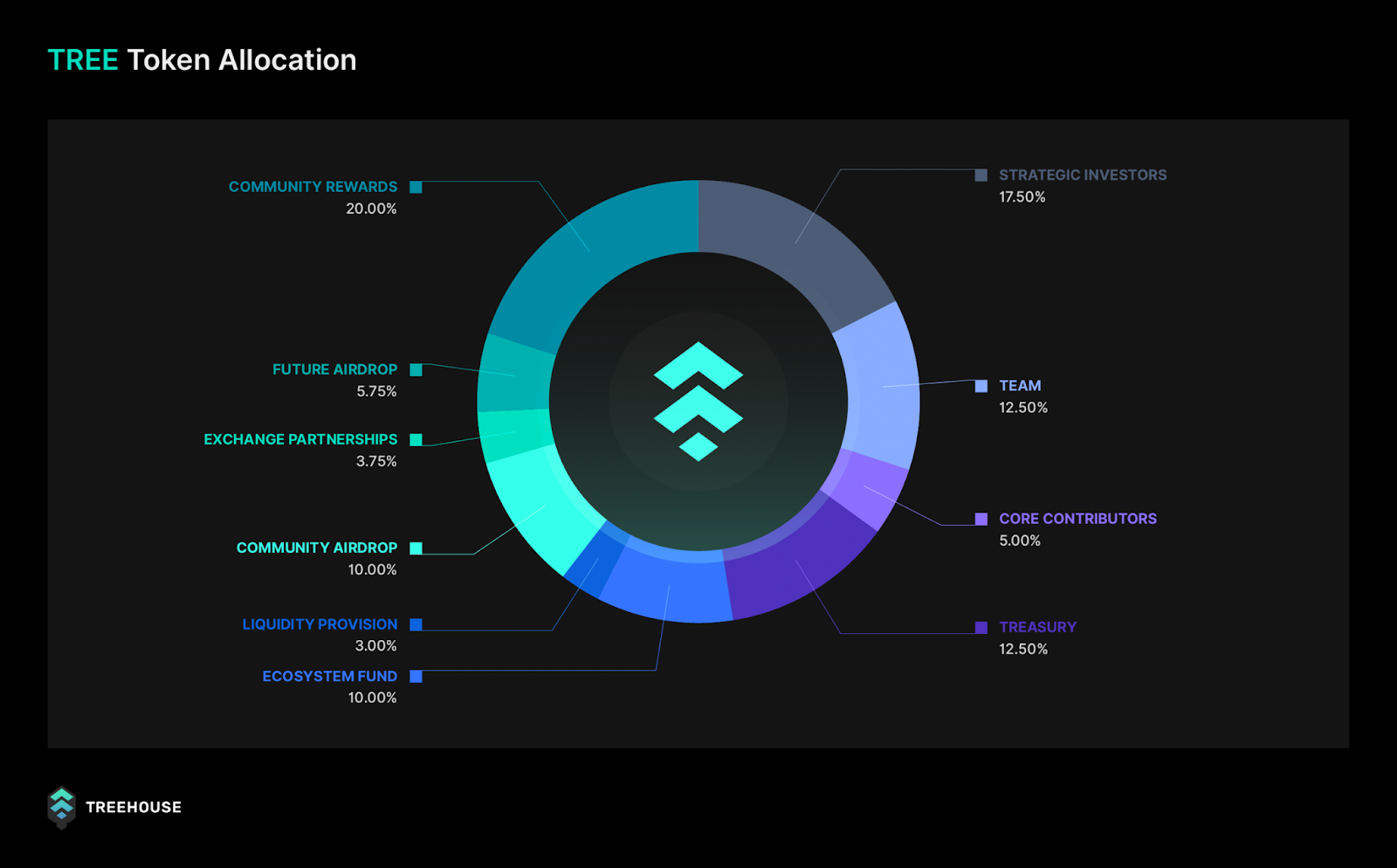
TREE Token
Token Details
Token Name: TREE
Token Symbol: TREE
Total Supply: 100,000,000 TREE tokens
Blockchain: Ethereum (ERC-20)
The
TREE token is the native utility token of the Treehouse protocol. The token is used for a variety of purposes, including:
-
Paying for DOR data: When smart contracts or businesses use Treehouse’s DOR benchmark data, they pay a small query fee in TREE tokens. This helps generate revenue for the protocol and ensures the fair use of its data infrastructure.
-
Staking by panelists: To maintain the integrity of DOR rates, panelists (the entities who submit rate data) are required to stake TREE tokens or tAssets. This ensures they have skin in the game and are motivated to submit accurate data.
-
Earning rewards: After each data submission round (or “observation period”), TREE tokens are distributed as rewards to both panelists and delegators based on how accurate the submitted rates were.
-
Governance: Holding TREE also gives you the power to vote on key protocol decisions like adjusting parameters, upgrading the system, or changing how rewards are distributed.
-
Funding innovation: Through the Treehouse decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), TREE tokens are also allocated as grants to support partnerships, developer tools, and new products built on top of the protocol.
Conclusion
Treehouse is addressing a key challenge in DeFi by creating the foundation for fixed income products in the crypto space. With innovations like tETH, the TESR Curve, and the DOR mechanism, it aims to bring more predictability to yields, make it easier to compare rates, and create more advanced financial products on-chain.
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.