The Bitcoin Halving stands as one of the most significant and predictable events in the financial world, a mechanism hardcoded into the protocol that fundamentally recalibrates the asset's economic engine. Occurring approximately every four years, it refers to the scheduled 50% reduction in the block reward granted to miners, effectively slashing the rate of new Bitcoin supply. This pre-programmed event is more than a technical curiosity; it is the core of Bitcoin's disinflationary monetary policy, designed to enforce digital scarcity and challenge traditional inflationary finance. With the fourth and most recent halving taking place in April 2024, reducing the reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC, the event continues to shape market cycles, mining economics, and long-term investment theses. This article delves into the origins and purpose of
the
halving, analyzes its profound impact on the cryptocurrency market, explores its implementation in other digital assets like Zcash, and identifies upcoming opportunities in the ever-evolving landscape of scarcity-driven assets.
What Is Bitcoin Halving? Understanding the Core Mechanism
Bitcoin Halving, sometimes termed "
the halvening," is a pre-programmed event embedded in the
Bitcoin protocol that cuts the block reward for miners by 50%. It operates on a simple yet elegant rule: after every 210,000 blocks are mined, which takes roughly four years given the network's target 10-minute block time, the subsidy for creating a new block is automatically halved. This process is entirely algorithmic and requires no human intervention or consensus decision, executed with the immutability that defines Bitcoin's code.
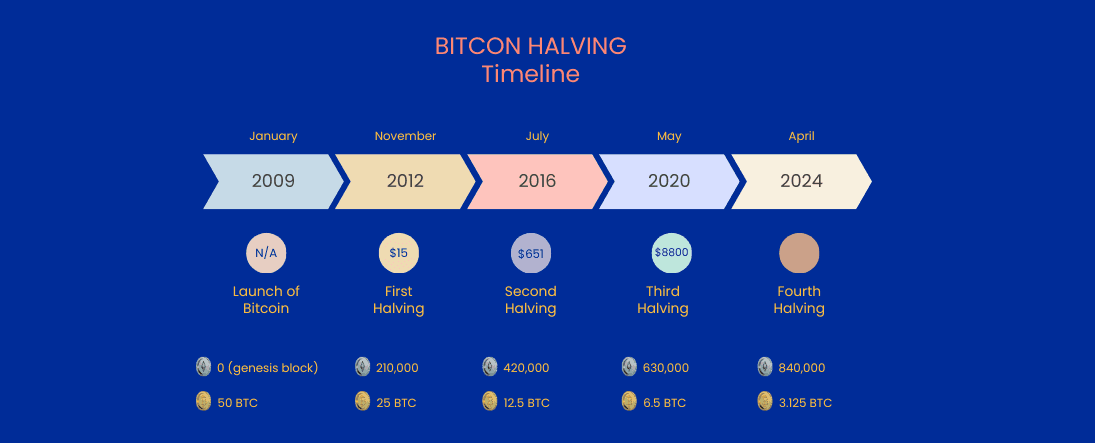
Initially, when Bitcoin's creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, mined the genesis block in 2009, the reward was set at 50 BTC per block. The first halving in November 2012 reduced this to 25 BTC, the second in July 2016 to 12.5 BTC, and the third in May 2020 to 6.25 BTC. The latest halving on April 20, 2024, ushered in the current era of 3.125 BTC per block. This process will continue until the total supply asymptotically approaches the hard cap of 21 million coins, estimated around the year 2140, after which miners will be compensated solely by transaction fees.
The code governing this is starkly simple. In Bitcoin's validation protocol, a function calculates the number of "halvings" that have occurred by dividing the current block height by 210,000. The subsidy is then calculated as 50 BTC divided by 2 to the power of the halving count, ensuring the reward trends toward zero over decades. This creates a transparent and predictable emission schedule, a radical departure from the opaque and discretionary monetary policies of central banks.
Why Was It Designed?
The halving mechanism was not an incidental feature but a deliberate design choice by Satoshi Nakamoto to solve core economic problems. Its primary purpose is to control inflation and enforce scarcity in a digital realm where replication is costless. By systematically reducing the flow of new coins, Bitcoin's protocol mimics the extraction of a precious resource like gold, where new supply becomes increasingly difficult and expensive to obtain over time. This counters the inflationary nature of fiat currencies, which central banks can produce in unlimited quantities.
Nakamoto explicitly framed this design in the context of traditional monetary failure. In a 2009 comment, they wrote, "The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust." The halving mechanism builds trust in code rather than institutions. It algorithmically guarantees that Bitcoin's inflation rate will fall over time. Following the 2024 halving, Bitcoin's annual inflation rate dropped to approximately 0.85%, lower than the natural growth rate of gold's above-ground stock. This decreasing supply growth, meetingpotential rising demand, forms the foundational economic thesis for Bitcoin's long-term value appreciation.
Furthermore, the halving schedule serves critical network security and decentralization functions in the early decades.The initially high block subsidy incentivizes a global, competitive mining industry to bootstrap and secure the network before a robust transaction fee market naturally develops. It ensures that security expenditure (hash rate) is funded by predictable, protocol-issued coins, making the network resistant to attack during its infancy. The gradual transition from block subsidy to transaction fees is a carefully engineered phasing-out of initial distribution, aiming for a mature network secured by its own utility.
What Impact Will Bitcoin Halving Have on the Cryptocurrency Market?
The impact of a Bitcoin halving ripples through every layer of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, from miner economics to global investor psychology. Its most anticipated effect is on Bitcoin's price, driven by the basic supply-demand dynamics of Economics 101. Historically, each halving has preceded a monumental bull market, though the causal relationship is complex and interwoven with broader market factors.
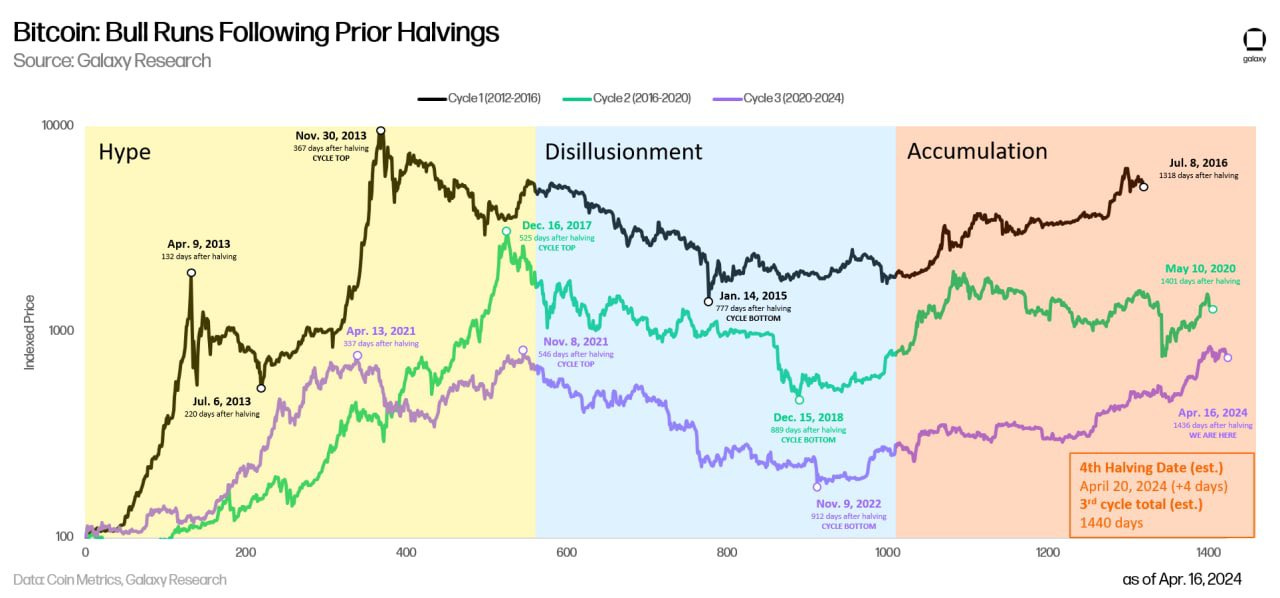
Historically, the twelve to eighteen months following a halving have seen exponential gains. After the 2012 halving, Bitcoin's price soared by over 9,500%. The 2016 halving was followed by a 3,400% increase, leading to the late-2017 peak near $20,000. The 2020 halving set the stage for a 652% rally that culminated in a then all-time high near $69,000 in November 2021. These patterns have cemented the halving as a central narrative in crypto market cycles. Analysts following models like the Stock-to-Flow, which links price to scarcity, have used halvings to project long-term price targets, with some predictions for this cycle reaching between $120,000 and $150,000, or even challenging $200,000 under strong macro conditions.
However, the 2024 halving cycle is demonstrating unique characteristics, suggesting "this time is different". One year post-halving, Bitcoin's price percentage growth is the weakest in its history compared to similar periods in past cycles. This muted performance coincides with heightened macroeconomic uncertainty and a shift in market structure. The unprecedented success of U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs, which attracted over $30 billion in inflows prior to the halving, introduced a massive, sustained source of institutional demand that may have front-run the typical post-halving rally.Consequently, Bitcoin's 60-day price volatility has plummeted from over 200% in 2012 to around 50%, indicating maturation and potentially more stable but moderate returns.
For miners, the halving is an immediate profitability shock. Their primary revenue stream is cut in half overnight, forcing an industry-wide efficiency drive. Miners with high operational costs or outdated equipment are squeezed out, leading to consolidation and geographical redistribution to regions with cheap, often renewable, energy. Network security, measured by hash rate, initially faces pressure but has historically recovered and grown as efficient miners expand and technology improves. Post-2024, the hash rate hit new all-time highs, but with the price not appreciating proportionally, miner margins have been severely compressed. This underscores a growing tension between network security and miner economics, increasingly reliant on transaction fees. The launch of protocols like Runes briefly spiked fee revenue post-halving, but sustaining high fees is critical for miner incentives as the block subsidy continues to diminish.
What Other Cryptocurrencies Have a Halving Besides Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin pioneered the halving mechanism, several other cryptocurrencies, primarily those using Proof-of-Work(PoW), have adopted similar disinflationary models. The most significant contemporary example is Zcash (ZEC), which underwent its own halving in 2025.
Zcash (
ZEC
): Zcash's halving reduced its block reward from 3.125 ZEC to 1.5625 ZEC, mirroring Bitcoin's supply schedule but within a distinct ecosystem focused on privacy. The 2025 Zcash halving was accompanied by a remarkable price surge of 1,172% year-to-date, pushing its price to $589. This performance was driven by a confluence of factors beyond mere scarcity: growing institutional adoption (evidenced by vehicles like the Grayscale Zcash Trust), technological upgrades including a shift towards a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) component, and its unique value proposition of shielded transactions using zk-SNARKs. Approximately 27-28% of Zcash network activity utilizes these privacy features, attracting investors seeking confidentiality and ESG-aligned protocols due to its lower energy footprint compared to pure PoW chains.
Halving events are primarily associated with Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithms where the reward for validating a block of transactions is reduced after a predetermined time. Below are some of the mainstream PoW cryptocurrencies that experience cryptocurrency halving:
Litecoin (
LTC
): Litecoin is a hard fork of the Bitcoin blockchain and is often considered the "silver" to Bitcoin's "gold". Litecoin experiences halving. In Litecoin halving, the block rewards miners get for verifying and adding a block to the blockchain reduces by half every four years, like Bitcoin. Litecoin's halving occurs precisely after every 840,000 blocks, in contrast to Bitcoin's 210,000 blocks.
Nervos Network (
CKB
): Nervos Network is a public proof-of-work blockchain solution developed to address scalability issues in layer-1 networks, featuring a dual-layer infrastructure with layer-1 as the foundation and layer-2 called “Godwoken”. Nervos Network, as a proof-of-work blockchain, experiences block halving, during which the block rewards for miners mining Nervos' native token, "CKB," are reduced by 50%. Nervos Network block halving happens every four years.
Dash (
DASH
): Dash is an open-source Proof-of-Work cryptocurrency, originally known as Darkcoin. Dash was launched as a fork of Litecoin (which is a fork of the Bitcoin protocol). Dash blockchain also experiences block halving. Dash halving occurs every 4 years, which is approximately after every 210,000 blocks, and Dash miners’ block rewards are reduced by 50% after each halving.
Upcoming Major Halving and Trading Opportunity
The next major Bitcoin halving is projected to occur around April 2028, at block height 1,050,000, when the block reward will drop from 3.125 BTC to 1.5625 BTC. This event will further reduce Bitcoin's annual inflation rate, cementing its status as an asset scarcer than gold. For traders and investors, the halving cycle presents a framework for strategic planning, though past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Trading opportunities around the halving typically unfold in phases. The pre-halving period often sees accumulation by long-term believers anticipating a supply shock, potentially months in advance. The event itself is usually marked by volatility and "sell-the-news" reactions. The most significant opportunities have historically emerged in the year following the halving, as reduced selling pressure from miners (who must sell fewer coins to cover costs) meets accelerating demand. However, as the 2024 cycle shows, with markets maturing and institutional products like ETFs altering demand dynamics, this pattern may evolve. Investors should monitor key metrics such as hash rate trends, miner outflow data, exchange reserves, and the growth of the transaction fee market.
Beyond Bitcoin, Zcash's next halving is expected in 2028, reducing rewards to 0.78125 ZEC. This presents a more niche opportunity. Investors drawn to privacy coins and alternative scarcity narratives may find value in analyzing Zcash's adoption metrics, regulatory developments concerning privacy technology, and the success of its hybrid PoS system in the lead-up to its next halving. Nevertheless, these assets carry higher risk due to lower liquidity and greater regulatory uncertainty.
In conclusion, the Bitcoin halving is a masterclass in cryptographic economic design. It is a pre-committed, transparent mechanism that ensures scarcity, controls inflation, and rhythmically resets the market's economic assumptions. While its direct impact on price is debated and influenced by an expanding universe of macro and micro factors, its role in defining Bitcoin's sound monetary policy is undisputed. As the crypto market matures with institutional involvement and new financial products, the halving effects may manifest in new, more nuanced ways. Yet, its core promise, which is a predictable and diminishing supply in a world of monetary expansion, will continue to make it a cornerstone event for understanding and navigating the cryptocurrency landscape.
References:
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.