The cryptocurrency market, known for its exceptional volatility, offers the potential for significant gains but also carries substantial risks, with forced liquidation being one of the most feared scenarios for traders. In a single 24-hour period, the market can witness a staggering 284,000 traders face liquidation, resulting in total losses exceeding $881 million. Also referred to as being "liquidated" or "stopped out," this event represents an automated, involuntary closure of a trader's leveraged position by the exchange. It occurs when the market moves against the position to a point where the trader's initial capital is nearly entirely depleted, acting as a risk management mechanism for platforms that extend leverage. This article provides a comprehensive examination of forced liquidation, exploring its mechanics in both spot and futures markets, outlining practical risk management strategies, and reviewing the latest regulatory developments shaping the landscape of leveraged crypto trading.
Understanding Contract Trading (Futures and Margin)
To comprehend forced liquidation, one must first understand the concept of contract trading, which encompasses both futures and margin trading. These financial instruments allow traders to borrow capital from an exchange or other traders to open positions much larger than their initial investment would normally allow. This borrowed capital is what constitutes leverage, expressed as a multiplier (e.g., 10x, 25x, 100x) of the trader's original collateral. While this leverage can dramatically amplify profits, it equally magnifies losses, creating a scenario where a relatively small adverse price movement can jeopardize the entire position.
The mechanism requires traders to maintain a minimum level of equity in their position, known as the maintenance margin. This is a critical threshold. As the market price moves against a leveraged position, the equity—the value of the position minus any borrowed funds—decreases. If this erosion continues unchecked, the equity will fall below the required maintenance margin level. It is at this precise moment that the exchange's automated systems intervene to trigger forced liquidation. The exchange is motivated not by malice but by financial self-preservation; it must protect the borrowed capital it has extended before the losses consume the trader's initial collateral and begin to eat into the exchange's own funds.
What is Forced Liquidation in Crypto?
When trading futures, you need to pay a small amount of money according to a certain ratio as the security deposit for contract performance, which is called Margin. More specifically, the Margin required for starting your position is referred to as Initial Margin; while Maintenance Margin is a proportion of the position value to keep your position open. Once your Available Margin fails to cover the Maintenance Margin, your position will be forced-liquidated.
Initial Margin and Maintenance Margin are calculated with different formulas.
The figures are calculated differently across exchanges. Here, we focus on CoinCatch.
Initial Margin = Open Value * Initial Margin Rate; Initial Margin Rate = 1 / Leverage * 100%
Maintenance Margin = Open Value * Maintenance Margin Rate
Let’s apply these formulas to practice: Suppose User A selects Cross Margin and longs 1 BTC at the unit price of 40,000 USDT with a 100X leverage ratio, the Initial Margin = 40,000*1/100 = 400 USDT, which is also the minimum Margin that he must pay for starting the position.
According to the tiered system of Maintenance Margin, User A’s Maintenance Margin Ratio stands at 0.5%, which means that the Maintenance Margin = 40,000*0.5%=200 USDT. If his Maintenance Margin falls below 200 USDT, the position would be forced-liquidated.
Why is Forced Liquidation Important?
Forced liquidation serves several purposes in the crypto market. Firstly, it helps prevent traders from accumulating substantial losses beyond their initial investment or account balance. By closing leveraged positions that have fallen below the designated threshold, forced liquidation limits potential losses, safeguarding traders against further downside risks.
Secondly, forced liquidation helps maintain stability and fairness in the market. In highly volatile markets, sudden price fluctuations can lead to severe losses for both traders and the exchange. Implementing forced liquidation protocols ensures that traders do not default on their borrowed funds, protecting the financial integrity of the platform and preventing systemic risks.
Mechanism and Process of Forced Liquidation
Forced liquidation typically follows a specific process:
1. Margin Requirements:
Exchanges set margin requirements, which determine the threshold for forced liquidation. When traders enter leveraged positions, the exchange lends them funds to increase their trading power. If the value of the position falls below the margin requirements, the forced liquidation process is triggered.
2. Asset Sale:
Once forced liquidation is triggered, the exchange automatically sells the trader's assets at the prevailing market price. This ensures that the borrowed funds are repaid, minimizing the risk of default and protecting the interests of both traders and the exchange.
Risk Management Strategies and Forced Liquidation
Prudent risk management is the only reliable defense against forced liquidation. The cornerstone of this defense is the judicious use of leverage. While exchanges may offer extremely high leverage, seasoned traders understand that lower leverage significantly reduces liquidation risk by providing a much larger buffer against market fluctuations.
A second critical strategy is the consistent use of stop-loss orders. A stop-loss is a pre-set order that automatically closes a position at a specific price point, allowing a trader to define their maximum acceptable loss on a trade. By setting a stop-loss at a level
before one's liquidation price, a trader can ensure they are stopped out on their own terms, preserving a portion of their capital and avoiding the total loss that comes with forced liquidation. It is a tool of discipline that allows traders to live to fight another day.
Other vital risk management practices include:
Diversifying one's portfolio across different assets to avoid being overly exposed to the volatility of a single cryptocurrency.
Continuous monitoring
of margin levels to ensure a comfortable buffer above the maintenance margin requirement.
Risking only a small percentage (e.g., 1-2%) of one's total portfolio on any single trade.
Staying informed about market news and trends to anticipate potential volatility.
Avoiding trading during periods of known high volatility, such as around major economic announcements or Fed meetings.
Exchange Tools for Risk Management
Recognizing the destructive impact of widespread liquidations, many centralized exchanges now provide traders with sophisticated risk management tools to help them visualize and manage their risk. These tools are often found on a dedicated "Risk Management" or "Positions" page within the trading interface.
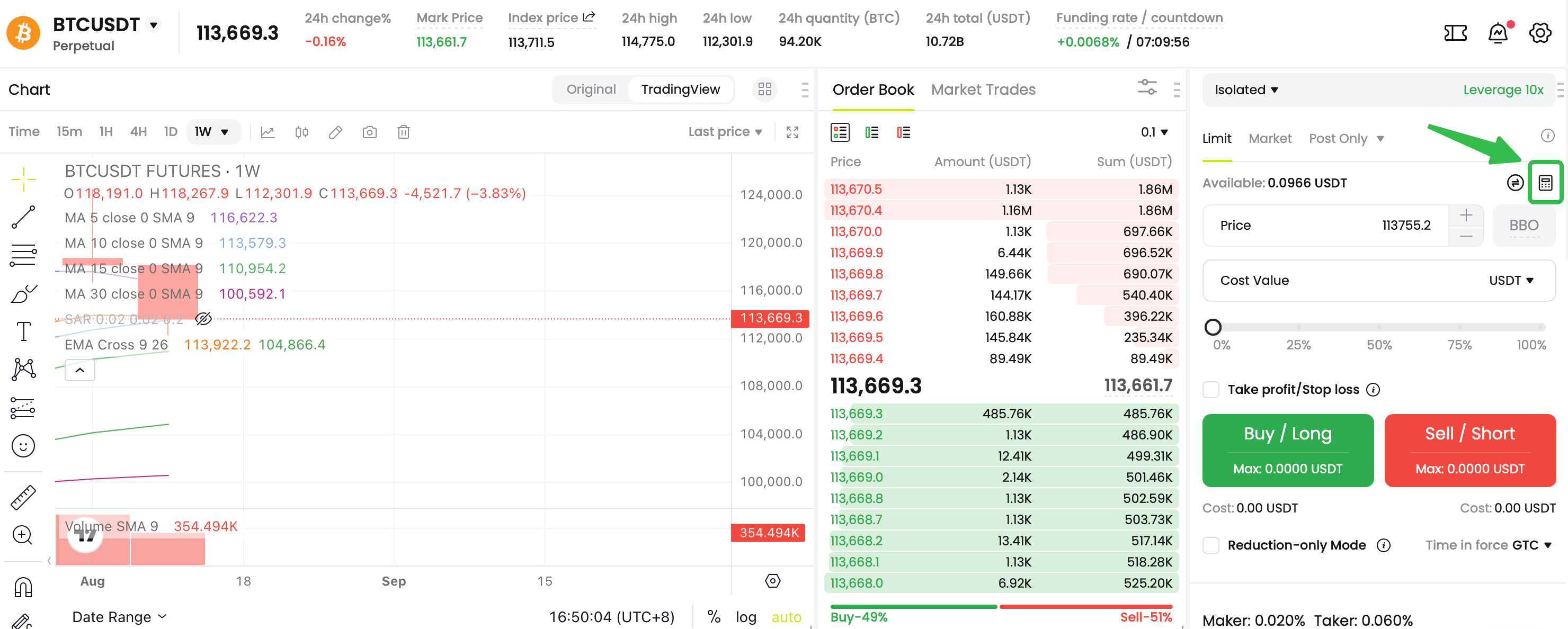
One of the most valuable tools is the
liquidation price calculator. Before even entering a trade, a trader can input their proposed leverage, entry price, and collateral amount. The calculator will then display the exact price at which their position will be liquidated. This allows for informed decision-making; if the liquidation price is too close to the current market price, the trader can choose to reduce their leverage or not enter the trade at all.
CoinCatch Futures Calculator: Futures Trading–
USDT-M Futures
(COIN-M Futures)–Trading Area
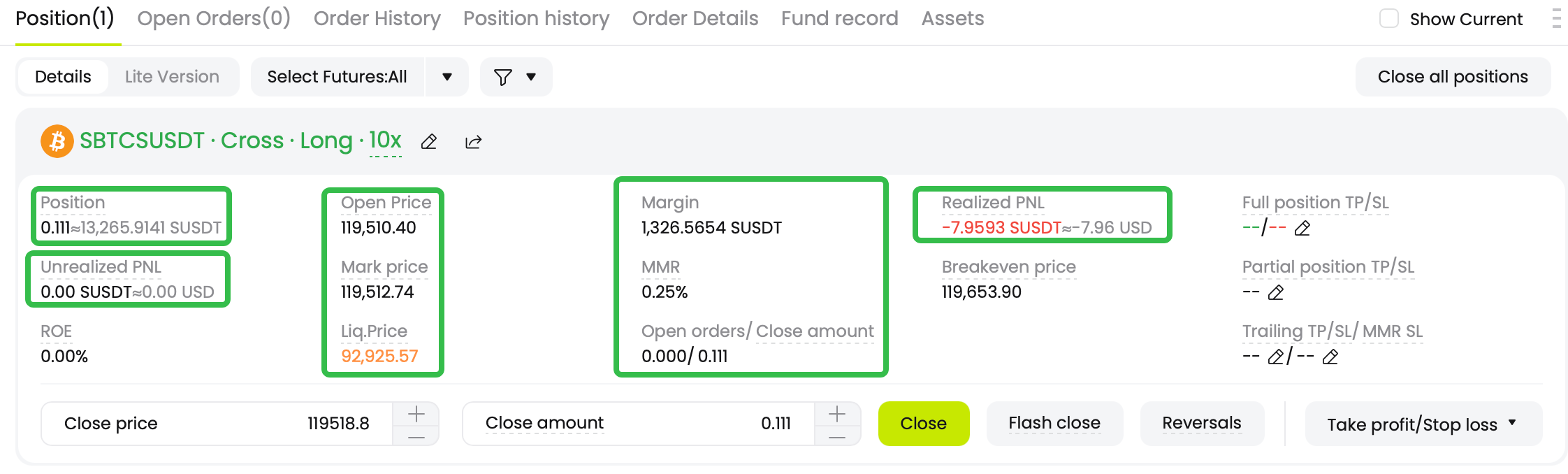
Other essential tools include
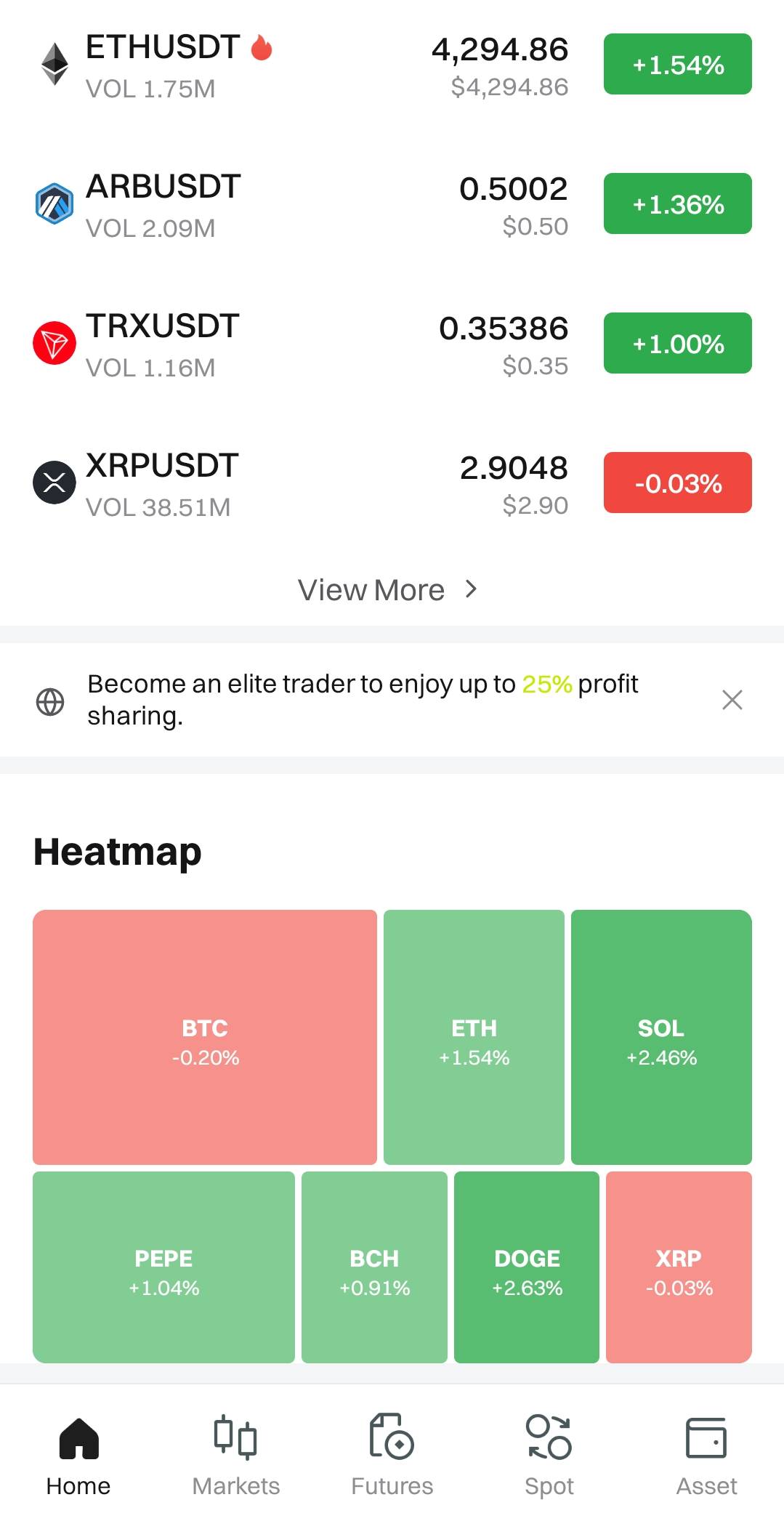
real-time position monitors that display crucial metrics like margin ratio and unrealized PnL, and liquidation heatmaps. These heatmaps visualize the concentration of liquidation orders across different price levels for an asset. By revealing these levels, they can serve as a warning to traders who might be opening positions with liquidation prices clustered in these high-risk zones, which can act like magnets during a market move.
CoinCatch
Real-time Position Monitors Section:
CoinCatch Heatmap(App):
Conclusion
Forced liquidation represents a fundamental aspect of trading with leverage, acting as the ultimate risk control mechanism for exchanges but often resulting in devastating losses for unprepared traders. It is the point where a trade fails catastrophically. As the recent regulatory actions in South Korea demonstrate, the risks are real and widespread, affecting both individual traders and the stability of the broader market.
However, this outcome is not an inevitability. Through a disciplined approach centered on moderate leverage, the unwavering use of stop-loss orders, and a thorough understanding of the tools provided by exchanges, traders can significantly reduce their exposure to this risk. The market will always be volatile, but a trader's response to that volatility need not be. The key to longevity in crypto trading is not maximizing potential gains in a single trade, but preserving capital over the long term. By prioritizing risk management above the allure of outsized returns, traders can navigate the turbulent crypto markets with greater confidence and resilience, ensuring they remain active participants rather than becoming another liquidation statistic.
References:
CoinGlass. How to Avoid Liquidation in Cryptocurrency Trading?. Retrieved August 21, 2025, from https://www.coinglass.com/learn/learn-152
Bitcoin Insider. The Spot Margin Services of Maker (MKR) Will Be Temporarily Closed! Retrieved August 21, 2025. https://www.bitcoininsider.org/article/283345/spot-margin-services-maker-mkr-will-be-temporarily-closed
CoinW Help Center. (2024, July 12). How to Reduce the Risk of Forced Liquidation. Retrieved August 21, 2025. https://coinw.zendesk.com/hc/en/articles/22143035901977
CoinEx. (2022, Feb 5). Determine the Right Margin and Margin Rate to Avoid Forced Liquidation! Retrieved August 21, 2025. https://www.coinex.com/en/academy/detail/142-how-to-calculate-margin-and-margin-rate?pId=31&sId=51
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.