On December 19, 2025, the Bank of Japan (BoJ) announced a significant policy decision, raising its benchmark short-term interest rate by 25 basis points to 0.75%, marking the highest level in thirty years. This unanimous decision was the first interest rate hike since January 2025 and indicates a readiness to implement further increases, supported by sustained inflation exceeding target levels and improving wage growth. The decision marks a decisive shift away from Japan's previous ultra-loose monetary policy, narrowing the interest rate differential with other major economies and contributing to a strengthening of the yen.
This policy change has immediate implications for global markets, including cryptocurrencies. On the day of the announcement, Bitcoin experienced increased volatility, trading around the $84,000 support level, reflecting heightened sensitivity to macroeconomic developments. The move is also accelerating the unwinding of the yen carry trade, reducing liquidity in risk assets and leading to increased selling pressures. While short-term volatility has increased and downside risks remain for Bitcoin and the broader crypto markets, these developments may also influence the longer-term perception and integration of cryptocurrencies within traditional financial frameworks.
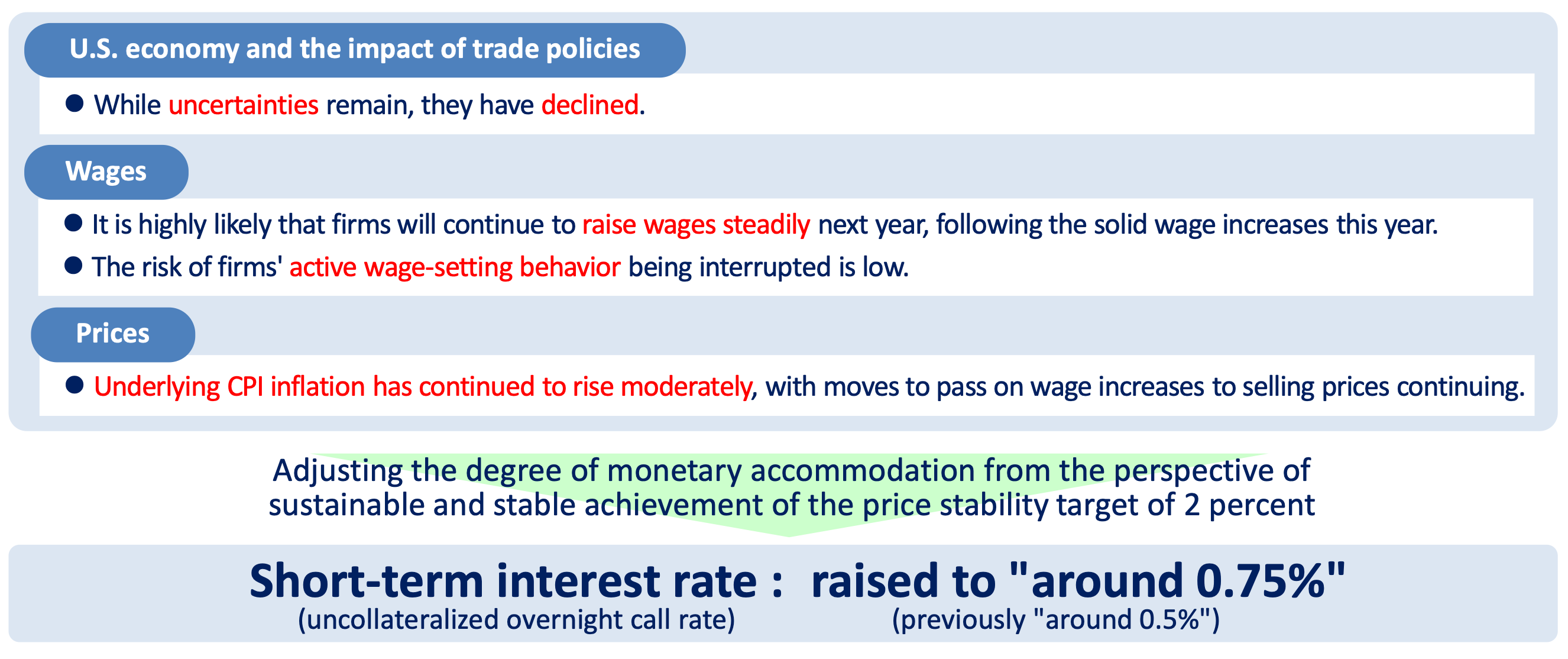
A Decades Long Negative Interest Rate Policy Ends
On December 19, 2025, the Bank of Japan announced an increase in the policy rate from 0.50% to 0.75%, aligning with market expectations of a 98% probability prior to the decision. This rate hike represents the latest step in a series of gradual normalization measures, driven by persistent inflation that has remained above the 2% target for nearly four years, along with strong wage growth signals from recent surveys. Governor Kazuo Ueda and the board highlighted the high likelihood of sustained moderate wage-price dynamics, supporting the decision despite some signs of economic softness.
Unlike previous rate increases that surprised markets, this move was thoroughly communicated in advance. Nevertheless, its confirmation led to notable market reactions. Japanese government bond yields increased sharply, with 10-year JGB yields surpassing 2% for the first time in decades, reflecting concerns about fiscal pressure resulting from higher borrowing costs in the context of Japan’s substantial public debt. The Japanese yen experienced a modest appreciation following the announcement, although gains were limited as the rate hike had largely been anticipated.
In the cryptocurrency sector, the immediate market response was subdued and cautious. Bitcoin declined toward $84,000 intraday, extending its weekly losses amid broader risk-off sentiment. The decision underscores a tightening global monetary landscape, even as some other central banks adopt easing policies, which has constrained the liquidity conditions that contributed to the rally in cryptocurrencies during 2025.
The Shift's Main Driver: Global Liquidity Drain
The yen carry trade, which is borrowing funds in low-cost Japanese yen to invest in higher-yielding assets abroad—has been a significant component of global financial markets since the 1990s. Japan's extended period of negative interest rates and quantitative easing created favorable conditions: near-zero borrowing costs, a stable or depreciating yen, and substantial yield differentials compared to U.S. and emerging market assets. Over time, this strategy has led to the accumulation of trillions of notional exposure, with hedge funds, financial institutions, and retail investors deploying proceeds into U.S. equities, Treasuries, emerging market bonds, and alternative assets such as cryptocurrencies.
The decision to raise interest rates in December directly impacts these positions. Higher yen borrowing costs, combined with expectations of yen appreciation, increase the cost of repaying foreign loans. According to interest rate parity principles, a narrowing or reversing yield differential tends to strengthen the currency, attracting capital inflows and challenging existing short-yen positions. As the profitability of carry trades diminishes, market participants are likely to unwind these positions rapidly, selling foreign assets, repurchasing yen, and repaying loans, resulting in a synchronized outflow of liquidity from recipient markets and exerting downward pressure on asset prices.
Historical examples include previous Bank of Japan tightening cycles in 2006-2007 and the abrupt exit from yield curve control (YCC) in 2023, both of which triggered sharp yen appreciations and risk-off episodes. The current cycle's rate hikes have already contributed to increased market volatility during the summer, with declines in cryptocurrency markets correlating with yen strength. The recent rate increase continues this trend: following the announcement, global equity futures declined, spreads on high-yield bonds widened, and liquidations in the crypto sector rose.
Regarding digital assets, indirect exposure amplifies these effects. While not all cryptocurrency leverage is directly tied to yen, the scale of the carry trade—estimated in trillions of dollars—has broad implications for liquidity across markets. Japanese retail investors, who are active in cryptocurrencies through platforms like bitFlyer, often fund leveraged positions through margin lending linked to domestic interest rates. Institutional carry strategies through prime brokers have also indirectly supported leveraged crypto investments. The unwinding of these positions leads to widespread deleveraging, disproportionately impacting assets with higher volatility and risk profiles.
Immediate Market Reactions: Crypto Under Pressure
Cryptocurrency markets exhibited cautious behavior on December 19. Bitcoin, which was trading around $84,500 prior to the announcement, experienced an intraday decline toward $84,000 and closed lower amid elevated trading volume. This movement extended a multi-week correction from levels above $90,000, with technical indicators signaling a bearish trend. Liquidations exceeded $200 million daily, primarily affecting long positions, as momentum-driven strategies triggered stop-loss orders.
Ethereum saw a more pronounced decline, testing the $2,800 level amid ongoing network inactivity and relative weakness. Most altcoins underperformed, with speculative tokens declining by 5-10% as risk aversion persisted. Bitcoin’s market dominance increased toward 58%, reflecting a shift toward the market’s perceived safest asset.
Sentiment indicators suggest a cautious mood: the Crypto Fear & Greed Index remained in extreme fear territory around 16-17, with social media activity turning bearish. On-chain data presented mixed signals; exchange inflows rose modestly, indicating some distribution, while whale accumulation continued at lower levels. Derivatives markets showed signs of deleveraging ahead of potential risks, with neutral funding rates and shrinking open interest, helping to mitigate cascading sell-offs but emphasizing caution.
Broader financial markets echoed this risk-off sentiment: Nasdaq futures declined, gold prices fell below $2,600, and high-yield crypto lending rates narrowed. The Japanese yen experienced modest gains, with USD/JPY approaching 148, suggesting initial unwinding; however, analysts cautioned that lagged effects could influence positions over the coming weeks.
Long-Term Fundamentals and Decoupling Potential
The Bank of Japan's normalization signals a transition to a post-emergency monetary environment, which challenges liquidity-dependent valuation models while emphasizing the unique characteristics of cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin's fixed supply offers a contrast to the risks of fiat currency debasement, especially in the context of rising global debt levels. As central banks proceed with normalization without triggering recessions, narratives around scarcity regain importance. Additionally, institutional demand such as from ETFs, corporate treasuries, and sovereign wealth funds, which drives structural interest independent of carry trade flows.
Ethereum's proof-of-stake consensus, scalability improvements, and layered applications (including DeFi and real-world assets) contribute to its utility-driven value proposition, potentially allowing decoupling based on real yields and wider adoption. The interest rate hike necessitates more sophisticated valuation approaches, integrating on-chain analytics, adoption trends, and macroeconomic factors. The resilience demonstrated by the crypto sector during this transition underscores its maturity, positioning it for sustained growth in a normalized monetary environment.
Market Outlook and Strategic Implications
The market response to this interest rate increase may be relatively brief, as the move has largely been anticipated and priced in. The primary focus now shifts to the Bank of Japan’s guidance regarding its monetary policy outlook for 2026. The central bank has announced plans to begin liquidating approximately $550 billion worth of ETF holdings starting in January 2026. Should indications of further interest rate hikes emerge, they could prompt a sustained and significant unwinding of carry trades, potentially leading to a decline in risk assets.
In the near term, the cryptocurrency market is likely to remain highly volatile. Market participants should monitor the USD/JPY exchange rate closely, as it serves as a key indicator of carry trade unwinding pressures. Bitcoin’s critical technical support levels are situated between approximately $80,550 and $72,367. If support within this range holds and the yen stabilizes, a temporary market rebound—often referred to as a "sell-the-news" rally—may occur.
From a longer-term perspective, this interest rate hike presents a significant test for cryptocurrencies as macro assets. It underscores that cryptocurrency prices are influenced not only by technological advancements and regulatory developments but also by broader macroeconomic factors such as global capital costs and sovereign bond yields. On one hand, the conclusion of a period of abundant global liquidity may challenge speculation-driven valuations. On the other, it could reinforce Bitcoin’s role as a long-term store of value amid concerns about global fiat currency expansion and inflation, especially as central banks navigate policy normalization processes.
The Bank of Japan’s interest rate increase signifies more than a mere adjustment in borrowing costs; it marks the end of an era and establishes new conditions for the cryptocurrency market. A new phase has begun, characterized by reduced liquidity that is more aligned with the broader global macro-financial environment.
Conclusion
The Bank of Japan’s long-awaited departure from negative interest rates is more than a monetary policy footnote. It is a profound reminder that cryptocurrencies, for all their disruptive potential, operate within and are indelibly connected to the global financial ecosystem. The expected 25 basis point hike on December 19, 2024, acts as a catalyst, forcing a painful but necessary reckoning with the realities of global capital flows, leverage, and correlation.
Reference:
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.