The Ethereum network stands at a pivotal juncture as it approaches one of its most significant upgrades in years. The
Fusaka upgrade
, scheduled for
December 3, 2025
, is poised to fundamentally reshape the network's scalability, economics, and value proposition. This hard fork arrives at a critical time for Ethereum, which has been navigating a complex landscape of macroeconomic headwinds, mixed institutional sentiment, and intense internal competition. In recent months, the market has witnessed a fierce tug-of-war between bearish pressures, including substantial ETF outflows and a notable wave of staking withdrawals, and bullish catalysts, such as aggressive whale accumulation and a resilient DeFi ecosystem. The Fusaka upgrade, with its promise of near-zero-cost Layer-2 transactions and enhanced data availability, is not merely a technical improvement; it is a strategic maneuver designed to solidify Ethereum's dominance as the leading smart contract platform. This article will dissect the current multi-faceted battle between Ethereum's bears and bulls, analyze the potent mix of risks and opportunities, and provide a clear-eyed outlook on what the Fusaka era could mean for the network's future in the 2026 market cycle.

Analyzing Ethereum's Recent Performance
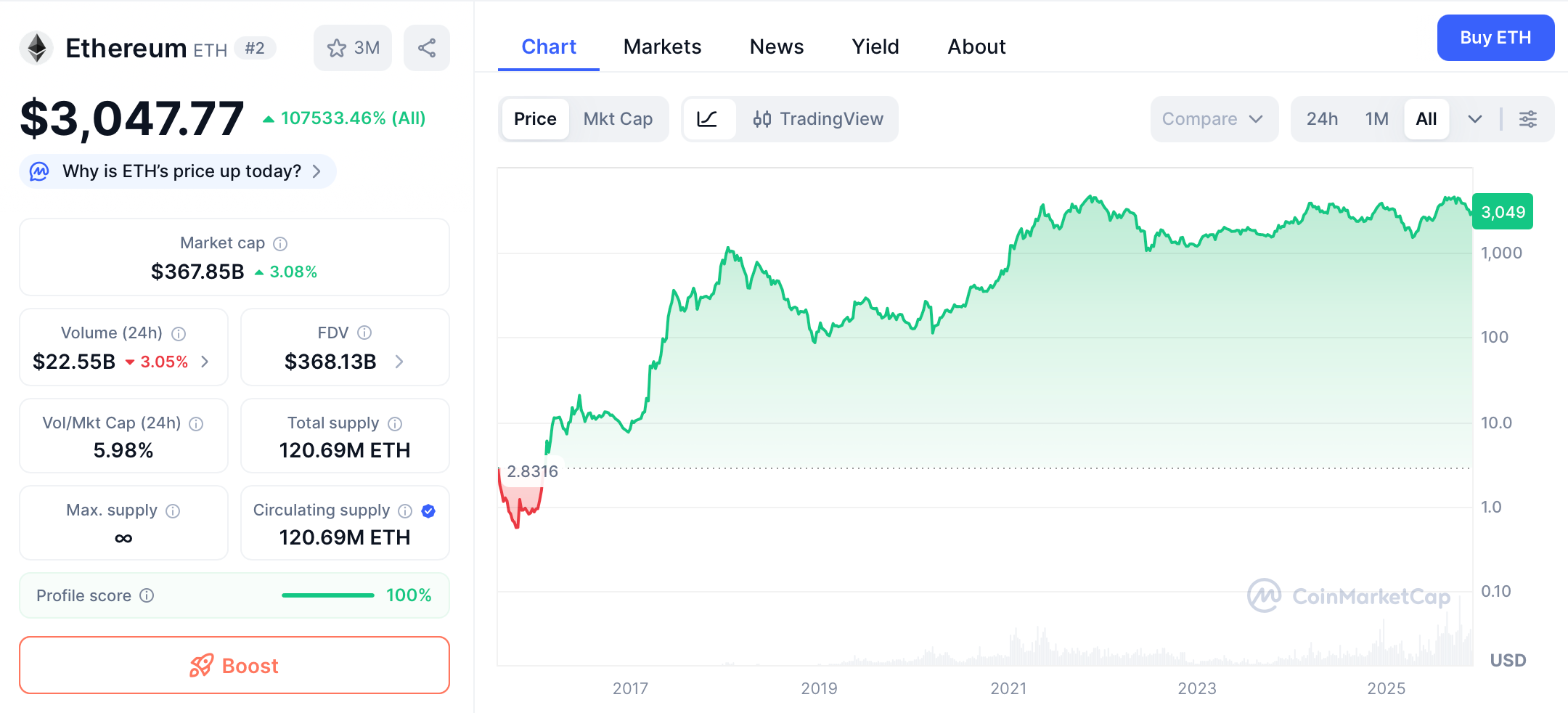
Ethereum price chart. Source: CoinMarketCap
In the third quarter of this year, the price of Ethereum climbed steadily along with rising market sentiment, surging from around $2,500 at the end of June to a peak of nearly $4,950 in late August. However, in October, a combination of macroeconomic and inherent market risks triggered an "epic crash." On October 11, the unexpected announcement by the US of additional tariffs on Chinese goods became the catalyst, triggering a global sell-off of risk assets, with the crypto market experiencing a sharp decline. The price of Ethereum once plummeted by more than 20% to a low of around $3,380. Although the market subsequently rebounded somewhat, liquidity gradually disappeared, and the overall trend remained downward. As of now, ETH is priced at around $3,000, a cumulative drop of more than 30% from its August high.
Macroeconomic Environment: The Federal Reserve signaled a hawkish stance in November, cooling market expectations for a December rate cut and significantly reducing risk appetite. The crypto market's boom in the third quarter largely benefited from institutional buying of new Ethereum ETFs – multiple Ethereum spot ETFs were launched during the summer, traditional investors rushed in, and several listed companies announced massive cryptocurrency purchase plans, creating strong buying support. However, in October, increased macroeconomic uncertainty led to a return of safe-haven funds to the US dollar and US Treasury bonds, rapidly depleting the marginal growth potential of the crypto market.
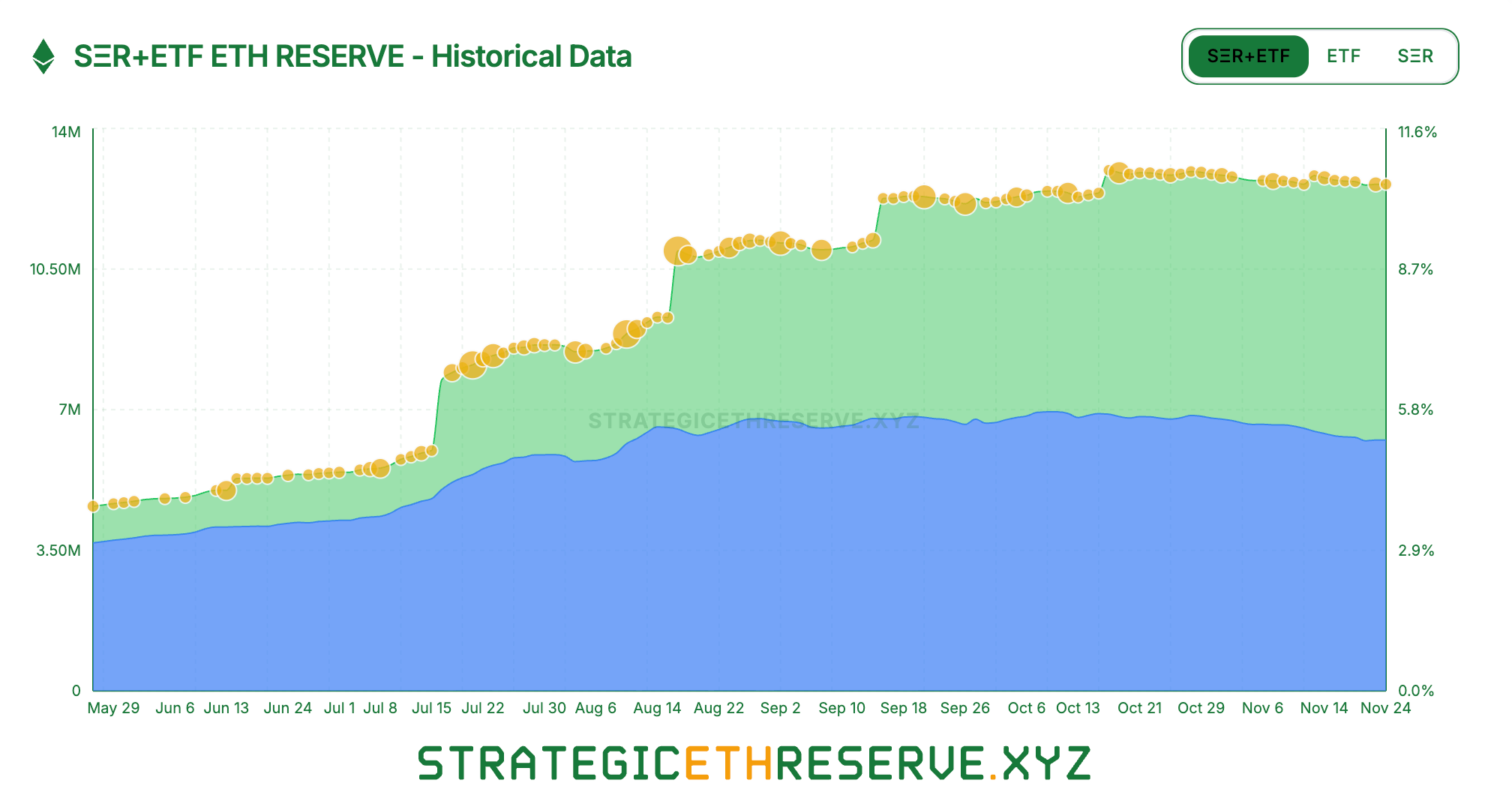
ETH DAT chart. Source: SΞR+ETF ETH RESERVE
DAT contraction: DAT (Depository and Acquisition) companies are seeing a contraction in their ETH purchases, and the sector is also showing signs of divergence. As of mid-November, DAT held approximately 6.24 million ETH in its strategic reserves, representing 5.15% of the total supply, with the pace of purchases slowing significantly in recent months. Among the major players, BitMine, a pioneer, is almost the only one still actively buying ETH: it added another 67,000 ETH in the past week alone. Another leading company, SharpLink, has stopped buying after purchasing 19,300 ETH in mid-October, with its holding cost at approximately $3,609, resulting in a paper loss. Smaller treasury companies are being forced to cut their losses. For example, ETHZilla sold approximately 40,000 ETH at the end of October to repurchase its own shares, hoping to narrow the price discount. The treasury industry has shifted from a period of uniform expansion to one of polarization: powerful giants are still managing to maintain their buying activity, while smaller players are struggling with liquidity constraints and debt repayment pressures, forcing them to reduce their holdings and cut losses.
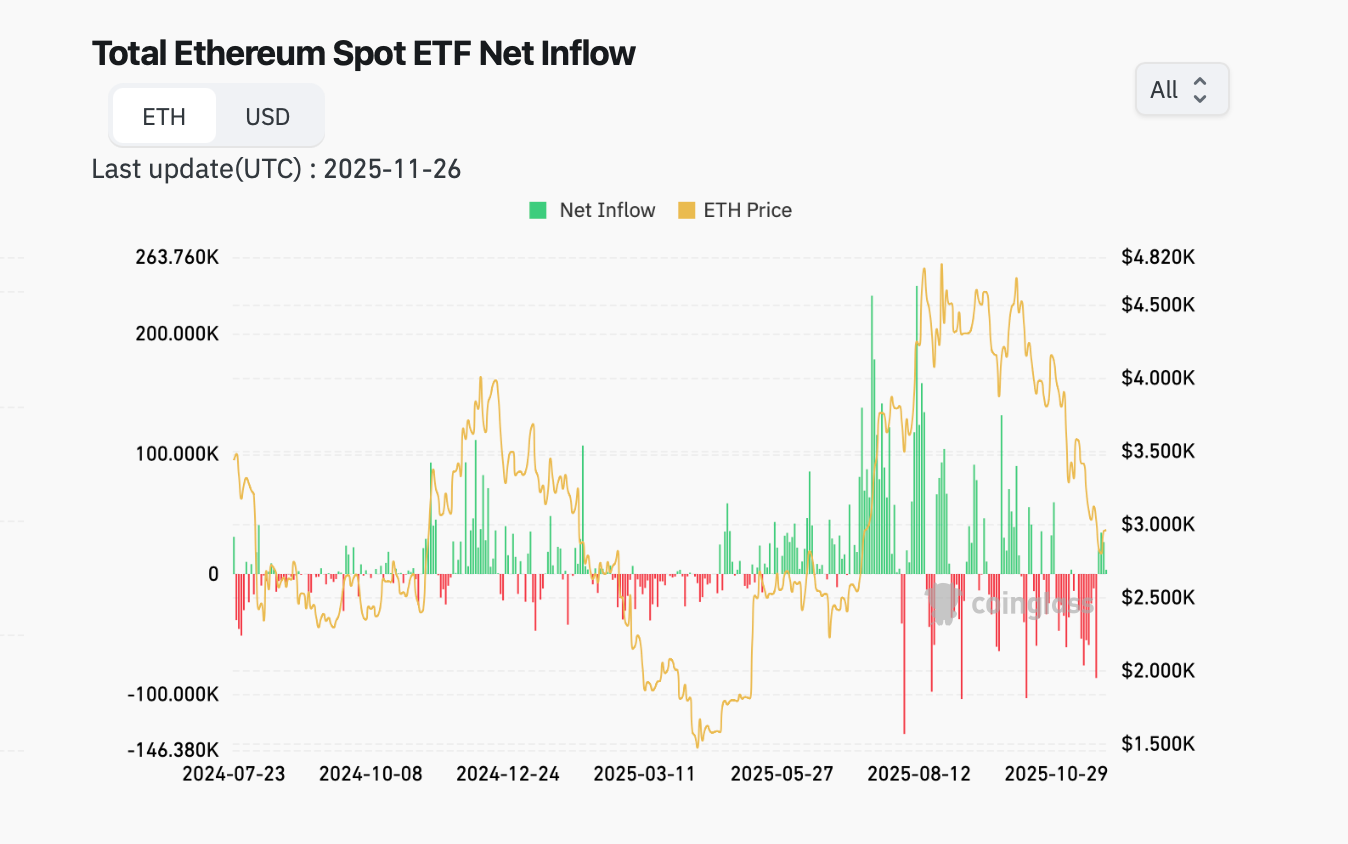
ETH ETF chart. Source: Coinglass
ETF outflows: In mid-November, the total holdings of Ethereum spot ETFs were approximately 6.34 million Ethereum (US$192.8 trillion), accounting for 5.19% of the ETH supply. However, this month saw a shift from net inflows to net outflows, with withdrawals significantly exceeding new inflows, and a single-day outflow reaching a maximum of US$180 million. This contrasts sharply with the steady daily inflows into ETFs during July and August. ETF investors are primarily focused on medium- to long-term investments, and the consecutive days of net redemptions indicate a weakening of demand for ETH from traditional financial channels. Their withdrawal not only directly reduces buying pressure but may also amplify short-term volatility.
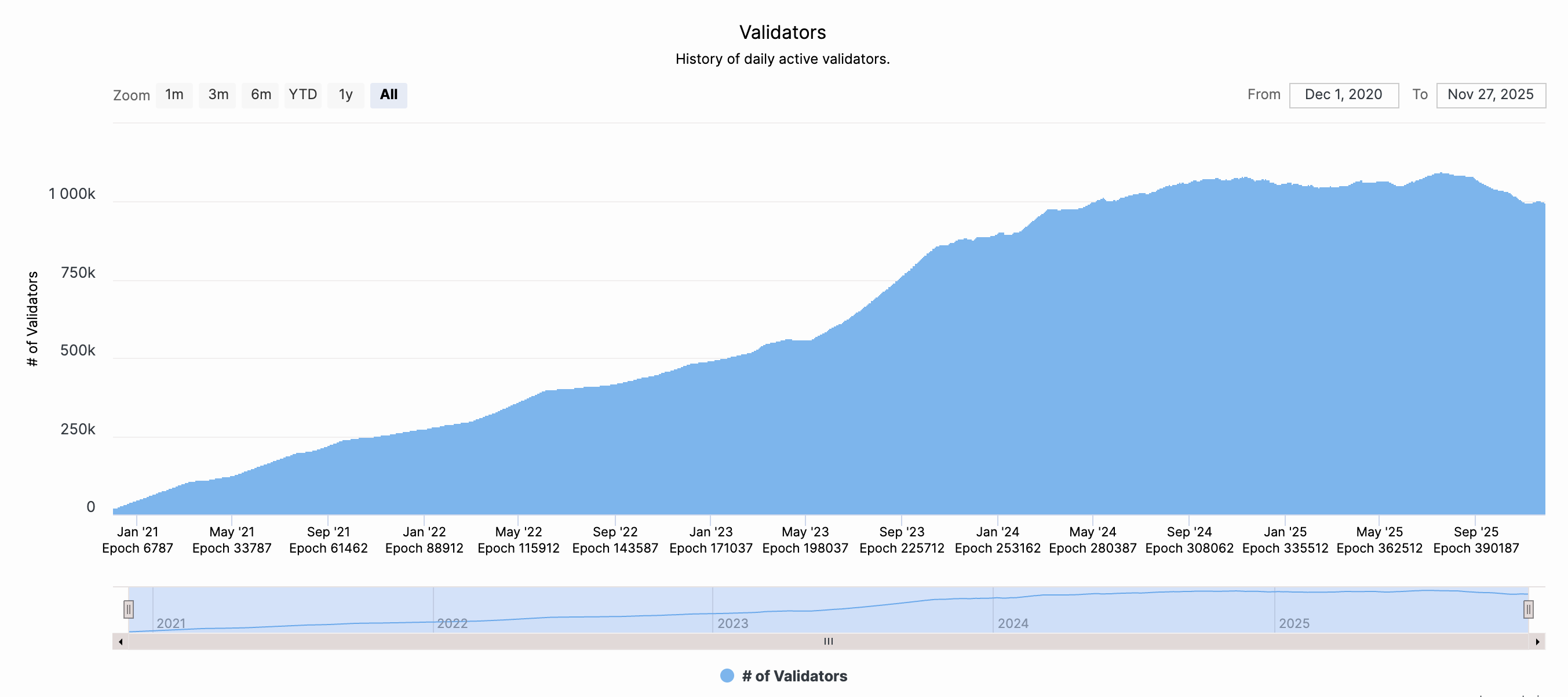
ETH validators chart. Source: beaconcha.in
Ethereum Staking Ebb and Flow: The Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism has become a central theme in Ethereum's market dynamics. In July 2025, data revealed a record queue of over 521,252 ETH (worth approximately $1.93 billion at the time) waiting to be withdrawn from staking. This surge, interpreted by some as a potential sign of profit-taking, was partially offset by continued new staking deposits, with 360,000 ETH entering the queue simultaneously. The situation intensified by September 2025, when over 910,000 ETH ($3.91 billion) were in the exit queue, a historical record that would take an estimated 45 days to process. Analysts offer a nuanced view: while this represents increased liquid supply, it may not be a direct signal of selling pressure. Instead, it could indicate a healthy ecosystem rotation, with institutions adjusting custody strategies or moving assets to pursue yield in DeFi protocols.
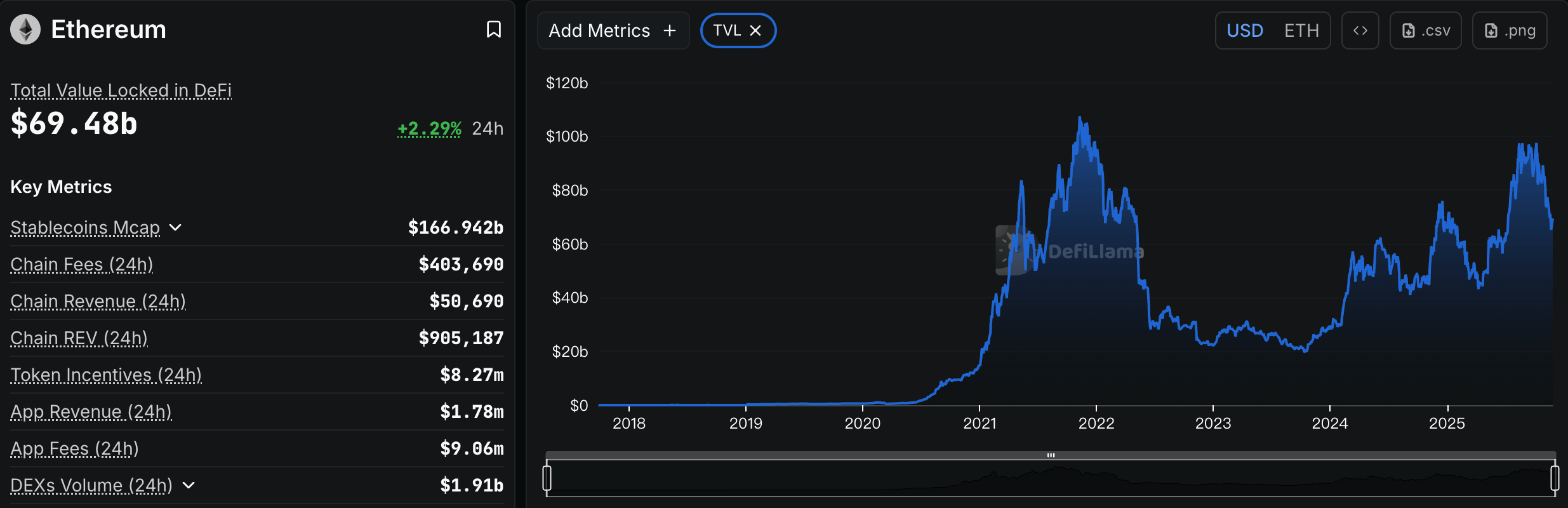
ETH TVL. Source: DefiLlama
Stablecoin and DeFi Oscillations: Stablecoins and DeFi Shocks: Problems within the Ethereum ecosystem were also exposed, further damaging investor confidence. On October 11th, the day of the crash, USDe collapsed due to the failure of its revolving lending arbitrage mechanism, falling to as low as $0.65. Although it quickly recovered to near $1, it triggered a chain reaction. Following this, multiple risk events occurred in the decentralized stablecoin sector: xUSD, issued by the Stream protocol, first suffered severe de-pegging due to the collapse of its underlying hedge fund; subsequently, USDX, using a similar strategy, also fell to $0.38 when liquidity was critical, posing a risk of being unable to redeem at a 1:1 ratio; another algorithmic stablecoin, deUSD, also failed to escape unscathed, falling below its peg price. These once-promising new stablecoins faltered under extreme market conditions, exposing the fragility and black-box risks of the "delta-neutral" stablecoin model under extreme market conditions. The successive failures of stablecoins dealt a heavy blow to DeFi. Starting in mid-October, several lending and yield aggregation protocols reported bad debts and a sharp drop in TVL (Total Value Linked). Morpho's USDC vault was forced to delist its strategies due to the zero value of its associated Elixir stablecoin pool, resulting in a loss of approximately 3.6% of the vault's assets. The established lending protocol Compound also faced bad debt pressure due to the collapse in the value of some long-tail stablecoins, triggering a liquidation crisis. The Balancer protocol suffered a hacker attack at the end of October, resulting in losses exceeding $100 million. These events triggered a continuous outflow of DeFi funds. As of early November, Ethereum's on-chain TVL had fallen from its year-to-date high of $97.5 billion to approximately $69.5 billion, evaporating over $30 billion in assets in just over a month.
The Bear Case: Macroeconomic Clouds and Lingering Concerns
Despite strong underlying technology, Ethereum faces several material headwinds that have fueled the bearish narrative.
Macroeconomic Uncertainty and Capital Competition: The crypto market remains highly correlated to traditional finance, particularly expectations around interest rates. Fears of a more hawkish Federal Reserve have repeatedly triggered capital flight from risk assets, including crypto. Furthermore, the competitive landscape for investor capital is intensifying. The success of Bitcoin ETFs has cemented BTC's status as the digital gold for institutions, while new entrants like Solana ETFs have demonstrated remarkable traction, with products recording 10 consecutive days of inflows and accumulating $510 million in net inflows, outperforming their Ether counterparts. This highlights a persistent challenge for Ethereum in capturing mindshare and capital in an increasingly crowded field.
Centralization and Technical Risks of Fusaka: Even the highly anticipated Fusaka upgrade carries its own set of risks. A primary concern among critics is that its core innovation, PeerDAS, could inadvertently lead to centralization. The protocol might concentrate data availability responsibilities into "super nodes" operated by large infrastructure providers, potentially undermining the network's decentralized ethos. Additionally, the upgrade's economic benefits are not guaranteed; they are contingent on widespread adoption and innovation by Layer-2 solutions. If the L2 ecosystem fails to leverage the new capabilities, the anticipated 5-10x increase in network revenue may not materialize, representing a significant execution risk.
The Bull Case: Fusaka Upgrade and Foundational Strengths
The bullish thesis for Ethereum rests on its formidable network effects and the transformative potential of the imminent Fusaka upgrade.
The Fusaka Upgrade as a Game Changer: Scheduled for December 3, 2025, the Fusaka hard fork is widely seen as a watershed moment. Its introduction of
Peer Data Availability Sampling (PeerDAS) is expected to expand block capacity by 400%, enabling near-zero-cost transactions on Layer-2 networks while maintaining robust security. This directly addresses Ethereum's most significant barrier to mass adoption: high fees. Furthermore, the upgrade includes a critical economic change through EIP-7918, which introduces a minimum data fee for L2s. Bitwise CIO Matt Hougan has highlighted that this mechanism could boost Ethereum's revenue capture by
5 to 10 times, creating a fundamentally stronger value accrual model for the ETH token. By enhancing scalability and creating a more predictable fee market, Fusaka aims to trigger a flywheel effect: lower costs attract more users and developers, leading to higher network activity, which in turn generates more fees and value for validators and stakers.
Network Effects and Institutional Endorsement: Ethereum's first-mover advantage in smart contracts has created a deeply entrenched ecosystem that is difficult to replicate. This resilience is reflected in ongoing institutional interest. Despite recent ETF outflows, the broader trend shows significant accumulation by large holders, or "whales." Data from November 2025 indicates that addresses holding between 10,000 and 100,000 ETH have collectively reached a balance of 21 million ETH, signaling strong conviction from deep-pocketed investors. This accumulation is interpreted not as short-term speculation, but as strategic positioning for the long term, often preceding major bull cycles. Institutions like Bitwise are recommending a
10-15% portfolio allocation to Ethereum post-upgrade, advocating for dollar-cost averaging (DCA) to navigate entry volatility.
Emerging Application Trends and Value Consensus: The Ethereum ecosystem continues to be a hotbed of innovation. Key trends such as the tokenization of real-world assets (RWA) and the maturation of DeFi are finding their most robust home on Ethereum. Moreover, a broader industry shift towards improving token value capture is underway, as seen with Uniswap's proposed fee switch. This aligns with Ethereum's own economic enhancements, creating a powerful narrative of tokens evolving from pure governance tools to assets with concrete economic benefits for holders.
Outlook and Conclusion
The path forward for Ethereum is a tale of two timelines. In the
short term, the market is likely to remain a battleground. The lingering effects of leveraged positions, potential selling pressure from unlocked staking queues, and competition from other crypto assets will continue to create volatility and test investor resolve. The immediate market reaction to the Fusaka upgrade itself is uncertain; should it encounter technical issues or slow adoption, it could temporarily dampen sentiment.
However, the
medium to long-term outlook, particularly looking toward 2026, is decidedly more constructive. The fundamental improvements brought by Fusaka are projected to materially improve Ethereum's utility and economic model. If the upgrade successfully delivers on its promises of low fees and high throughput, it could unlock the next wave of Web3 adoption, attracting a new generation of users and applications. Analyst projections, buoyed by this potential and ongoing whale accumulation, suggest Ethereum could target levels between
$4,500 and $8,000 in the next bull cycle, provided it maintains key support zones.
In conclusion, the Fusaka upgrade represents far more than a routine network improvement. It is a strategic catalyst arriving at a critical moment. While Ethereum must navigate a complex web of macroeconomic pressures and internal ecosystem challenges, its unparalleled network effects, ongoing institutional validation, and the profoundly scalability-enhancing nature of Fusaka provide a compelling counterweight. The current multi-faceted battle between bears and bulls is not a sign of weakness, but a reflection of Ethereum's central and contested role in the digital asset space. For investors and builders, successfully navigating this period requires a focus on the long-term horizon, looking beyond short-term price swings to the fundamental value being built. The activation of Fusaka on December 3rd may well mark the beginning of a new, more scalable, and economically sustainable chapter for the Ethereum network.
References:
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.