Beneath the volatile surface of cryptocurrency charts lies a critical, yet often misunderstood, force: market making. It is the invisible engine of digital asset markets, ensuring that when you want to buy or sell a token, there is someone on the other side of the trade. Without it, exchanges would be illiquid, prices would be wildly unstable, and the crypto ecosystem would struggle to function. In 2025, this niche domain is undergoing a profound transformation, moving from an opaque, often distrusted practice toward a more transparent and technologically sophisticated infrastructure layer. Recent developments, from the integration of open-source algorithms by major exchanges to groundbreaking research applying quantum computing to decentralized finance (DeFi), highlight this rapid evolution. This article demystifies crypto market making, exploring its fundamental mechanisms, the advanced technology that powers it, the key players shaping the industry, and the future trends that promise to redefine liquidity in the digital age.
What is Market Making?
Let’s begin with a fundamental definition of a market maker. A market maker is essentially an entity playing a critical role in pricing assets by discovering their fair value. Behind these ‘fair’ prices, a market maker is always present and prepared to both buy and sell the asset. This concept is universal across asset types.
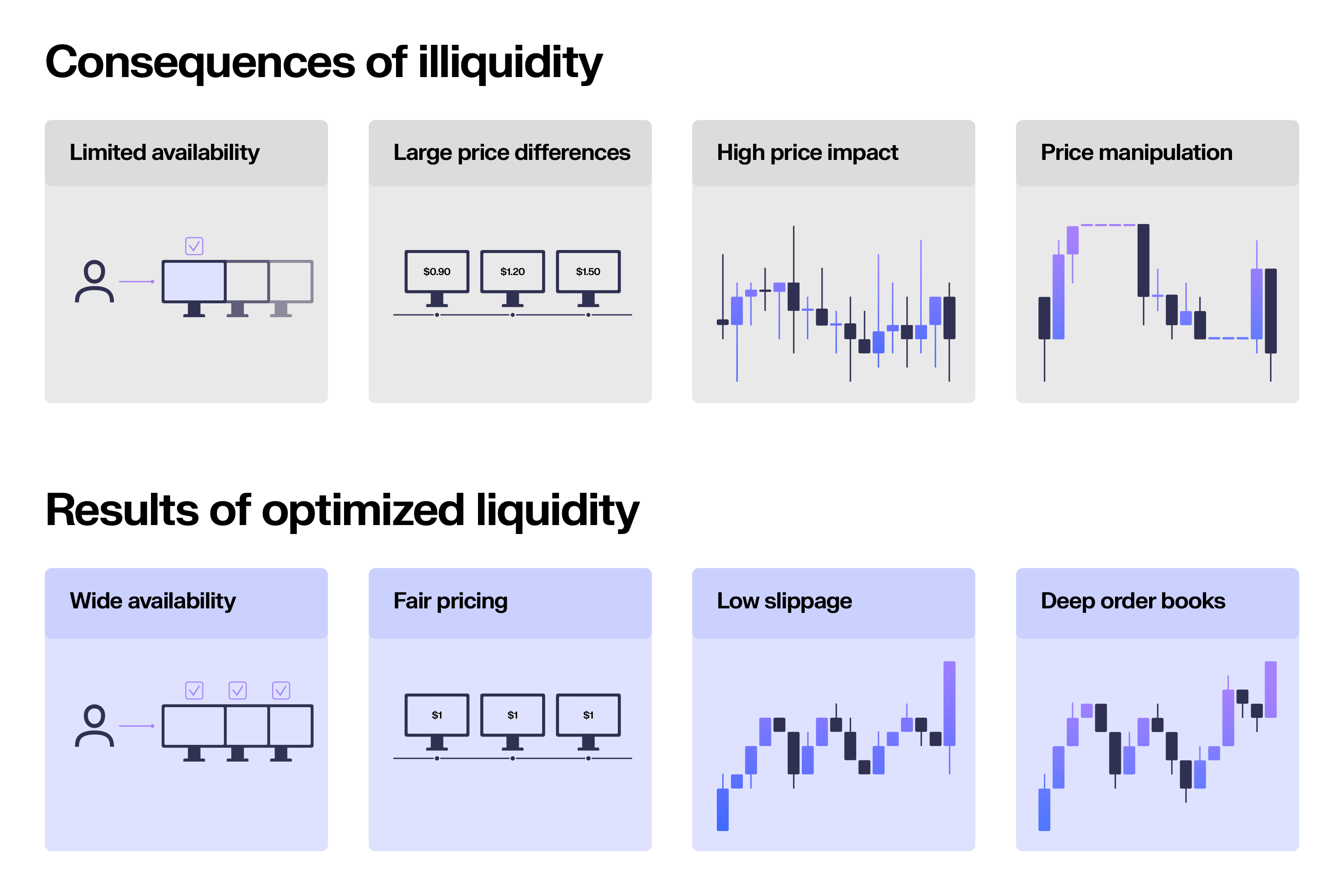
In traditional finance, consider a scenario involving a publicy traded company’s stock. Market makers actively contribute to ensure smooth trading for all participants, bringing value to both the investors and the company itself. To do so, market makers aim to increase the overall liquidity, which is the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold in the market without significantly impacting the asset’s price.
Suppose Company XYZ has its shares listed on a stock exchange. Market makers continuously allocate capital inside the order book to buy shares from sellers or sell shares to buyers at what they believe is the asset’s fair value. The presence of market makers helps maintain liquidity in the stock, which decreases assets’ volatility and price impact.
Highly liquid assets, like Company XYZ’s stock, can be readily bought or sold without causing significant price impact. The easier it is to buy or sell stock, the more liquid it is. This is because market makers facilitate trades even when there are no direct buyers or sellers at a specific moment. In turn, investors can enter or exit their positions in Company XYZ’s stock efficiently without experiencing major price disruptions.
What is Crypto Market Making?
At its core, what market makers do in crypto space is akin to traditional finance, with the added complexity of staying innovative with their service offerings, as one would expect from an actor in the dynamic digital asset space. Keeping the concept above of liquidity in mind, let’s look at how that translates within the crypto arena by taking the launch of a new token, $NEW, as an example.
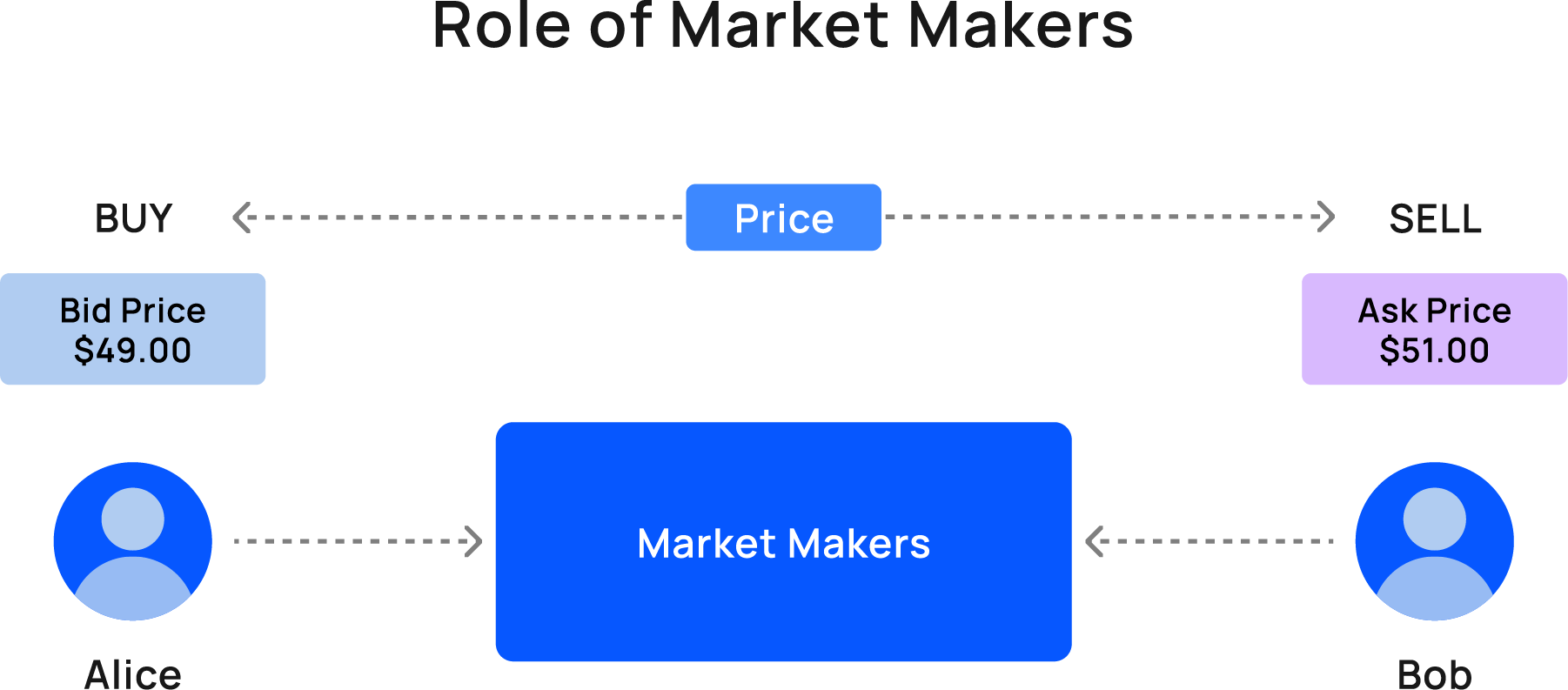
Right after its introduction (initial listing) to the market, there may not be many buyers and sellers, making it challenging for participants — let’s call them Alice and Bob — to find each other and agree on a price for $NEW tokens. This is where market makers come into play.
Here, market makers ensure a level of liquidity by providing continuous buy and sell orders for various cryptocurrencies. In this scenario, we could have Charlie act as a market maker who steps in to bridge the gap between Alice and Bob. Charlie offers to buy $NEW tokens from Alice at a price she finds acceptable and sell them to Bob for a price he deems fair, closing the difference between the prices of Alice and Bob, which is also called tightening the spread.
By doing so, Charlie facilitates trade and contributes to the overall liquidity of $NEW in the market. This means that participants like Alice and Bob can enter or exit the market at any time with relative ease, thanks to the presence of market makers like Charlie.
The role of market makers in pricing assets is closely tied to their responsibility to provide liquidity in the market. Not only are they prepared, but they are equipped to buy and sell assets, making it possible for all participants, including buyers, sellers, and the issuing company, to trade efficiently and effectively in both traditional finance and the crypto asset space.
How Market Making Works in the Crypto Ecosystem
Market making operates across two primary domains in crypto: centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs). On CEXs like Binance or Coinbase, professional market-making firms use high-tech algorithms to place vast numbers of buy and sell orders on the order book. These entities are often engaged by the exchanges themselves or by token projects seeking to ensure liquid trading for their assets from the moment of listing.
The process for a new token launch illustrates its critical importance. Initially, a new token lacks a natural pool of buyers and sellers. To solve this "chicken-and-egg" problem, token projects typically provide a portion of their native tokens to a market maker. The market maker pairs these tokens with a base currency like USDT and begins providing liquidity from the very first second of trading. While they cannot prevent the natural price discovery that occurs when a hyped token lists, they dampen extreme volatility and protect traders from excessive slippage during the initial trading frenzy.
In the realm of DeFi, market making has been democratized through Automated Market Makers (AMMs) like Uniswap. Here, liquidity is not provided via an order book but through liquidity pools where anyone can lock tokens into a smart contract. While this allows retail participants to act as liquidity providers, professional market makers still play a vital role in DeFi by providing deep liquidity and managing order books for decentralized order book (DLOB) exchanges, helping to narrow bid-ask spreads.
Technology Powering Modern Market Making
The image of a trader shouting on an exchange floor is entirely obsolete. Contemporary crypto market making is a discipline dominated by advanced technology and algorithms.
Algorithmic Trading: Sophisticated algorithms are the backbone of market making. They can execute passive strategies, patiently placing orders below and above the current market price, or active strategies that dynamically adjust to market volatility in real-time. High-frequency trading (HFT) strategies, which capture tiny price discrepancies across multiple platforms in milliseconds, are also employed, though these require low-latency infrastructure and are capital-intensive.
Risk Management and Inventory Management: A crucial technological component is the system that tracks the firm's overall exposure across various assets and exchanges. The goal is to remain "delta neutral," avoiding excessive risk by hedging positions and maintaining a balanced inventory. Effective risk management can significantly reduce potential losses, prioritizing long-term survival over short-term gains.
The Quantum Frontier: Cutting-edge research is pushing the boundaries further. A 2025 empirical study by Omnis Labs applied a Quantum Adaptive Self-Attention (QASA) module to the problem of portfolio rebalancing in DeFi AMMs. This quantum-classical hybrid model showed promising results, achieving a 13.99% return and a Sharpe Ratio of 1.76 in backtests, outperforming traditional machine learning models like random forests and gradient boosting. This points to a future where quantum-inspired algorithms could enhance the efficiency and stability of market-making strategies.
Leading Market Makers, Funding, and Innovative Projects
The crypto market-making landscape is dominated by specialized firms that have secured significant funding and trust.
Headlining Players and Financing: Established names like Wintermute and B2C2 are key liquidity pillars. In a sign of growing institutional confidence, Wintermute secured a bitcoin-backed credit line from the prestigious financial firm Cantor Fitzgerald in mid-2025, enhancing its ability to hedge risk and maintain broad market coverage. Around the same time, reports emerged that B2C2 was seeking to raise to $200 million in funding, partly to facilitate a reduction of its parent company SBI Holdings' stake, indicating investor appetite for mature crypto market-making ventures.
Open-Source and Accessible Solutions: A trend toward democratization is evident with the rise of projects like Hummingbot, an open-source market-making bot. In a significant move in September 2025, major exchange Bitget integrated Hummingbot, providing its users with a direct connector to deploy automated market-making and arbitrage strategies on its platform. This integration lowers the barrier to entry for smaller players and reflects a push toward greater transparency and standardization.
Innovative AMM Designs: On the DeFi front, research teams are proposing next-generation AMM designs to overcome current limitations. Paradigm's "Orbitals" concept, introduced in 2025, aims to support liquidity pools for thousands of stablecoins with higher capital efficiency than current leaders like Uniswap V3, using an n-dimensional sphere and nested tick mechanism.
The Future of Market Making: Predictions and Trends
The industry is rapidly evolving, driven by demands for greater transparency and technological innovation. The LO:TECH report outlines several key trends for the future. First, the industry is moving toward
standardized legal structures, akin to traditional finance's ISDA agreements, to clarify terms and build trust. Second,
evolving on-chain infrastructure, particularly DLOBs, will make market-making activity more auditable and transparent. Finally,
protocol-controlled liquidity, where a DAO or community treasury manages market-making assets, could better align incentives for long-term project health.
The integration with traditional finance is also expected to deepen. The growth of tokenized assets, including stocks and ETFs, will create new venues for market makers to operate. As seen in China's booming ETF market, increased participation from market makers leads to narrower bid-ask spreads, benefiting all investors. The future points to market makers evolving from tactical liquidity providers into trusted, transparent infrastructure partners essential for a mature digital asset market.
Key Considerations for Market Making on CEX
For projects and entities looking to engage with market makers on CEXs, several factors are critical. The 2025 LO:TECH report emphasizes that
reputation, transparency, and structural clarity are paramount when selecting a partner. Projects should seek market makers with a proven track record and demand real-time performance dashboards with clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). There is a growing preference for "fixed fee" structures over complex "option + loan" models, as the former offers cost transparency and reduces misaligned incentives that could lead to practices like wash trading or token dumping. Furthermore, projects must be wary of exchanges that demand excessive token payments for market-making services disguised as aggressive listing terms. The recent integration of tools like Hummingbot on major platforms also indicates a future where exchanges will offer more
native product support for market making, giving users more control and visibility into liquidity provision.
Conclusion
Market making is the essential glue that holds the cryptocurrency market together. It has evolved from a behind-the-scenes activity shrouded in skepticism to a professionalized field embracing open-source innovation, quantum computing research, and institutional capital. As the industry marches toward greater standardization and transparency, market makers are set to become integral, trusted components of the crypto infrastructure. Understanding their role, technology, and the trends shaping their future is no longer just for experts; it is fundamental knowledge for anyone serious about navigating the complex and dynamic world of digital assets. The invisible engine is being upgraded, and its newfound transparency will power a more efficient and robust financial system.
References:
CoinCatch Team
Disclaimer:
Digital asset prices carry high market risk and price volatility. You should carefully consider your investment experience, financial situation, investment objectives, and risk tolerance. CoinCatch is not responsible for any losses that may occur. This article should not be considered financial advice.